With growing concerns about fuel prices, climate change, and environmental sustainability, Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) have emerged as a popular solution. They combine the best of gasoline engines and electric motors, offering improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and a smoother driving experience.
In this guide, we’ll explore what HEVs are, how they work, their advantages, challenges, and future potential.
What is a Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)?
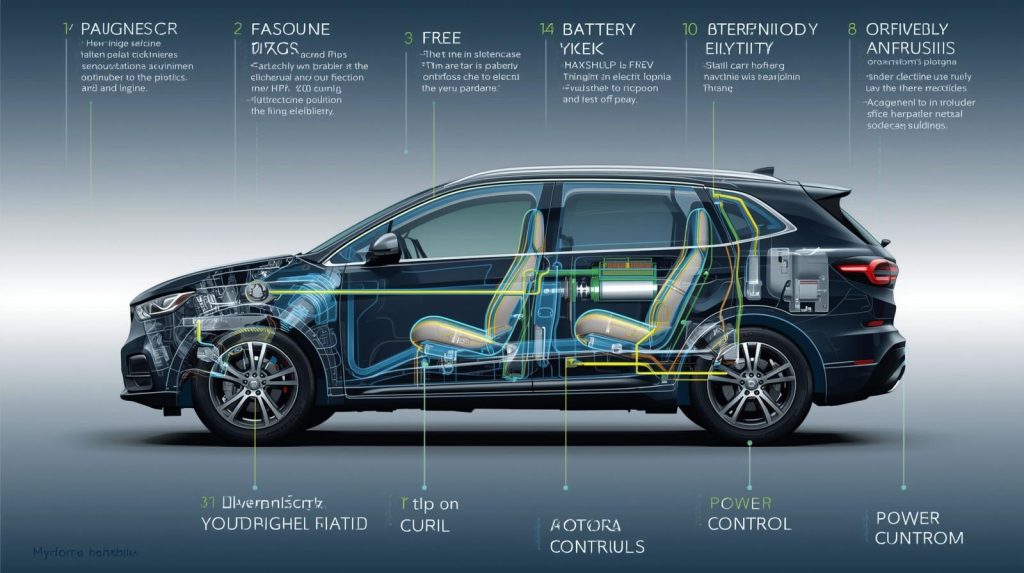
A Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) is a car that uses both a gasoline engine and an electric motor to provide power. Unlike Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) or Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), HEVs cannot be plugged in to charge. Instead, the electric motor is powered by a battery that is recharged through regenerative braking and the gasoline engine itself.
HEVs are designed to optimize fuel consumption by automatically switching between the electric motor and gasoline engine, depending on driving conditions.
How Do HEVs Work?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) work by combining a gasoline engine with an electric motor to power the car efficiently. At low speeds or during stop-and-go traffic, the electric motor powers the vehicle, saving fuel. At higher speeds, the gasoline engine takes over, while also helping recharge the battery.
HEVs use regenerative braking to capture energy when slowing down, which is stored in the battery for later use. This smart combination reduces fuel consumption, lowers emissions, and provides a smooth, eco-friendly driving experience.
HEVs operate using a dual power system:
- Gasoline Engine: Provides power for high-speed driving and long distances.
- Electric Motor: Supports acceleration and low-speed driving, reducing fuel consumption.
- Battery Pack: Stores energy generated through regenerative braking and the engine.
- Power Electronics/Controller: Manages the balance between gasoline and electric power.
When driving, the vehicle automatically switches between the electric motor and gasoline engine for maximum efficiency. For example:
- Low-speed city driving is often powered by the electric motor only.
- Highway driving uses the gasoline engine, sometimes with electric assistance.
This smart combination reduces fuel usage and minimizes emissions without compromising performance.
Advantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) offer several benefits that make them popular among eco-conscious drivers:
- Better Fuel Efficiency: Uses less gasoline by combining an electric motor with the engine.
- Lower Emissions: Produces fewer greenhouse gases than traditional cars.
- No Need to Plug In: The battery recharges automatically through regenerative braking and the engine.
- Smooth Driving Experience: Electric motor provides quiet and responsive acceleration.
- Cost Savings: Reduced fuel consumption lowers overall running costs.
HEVs are ideal for city driving and for drivers who want a fuel-efficient, environmentally friendly vehicle without fully switching to electric cars.
Challenges of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
While Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) are fuel-efficient and eco-friendly, they also have some challenges:
- Higher Upfront Cost: HEVs are more expensive than conventional gasoline cars due to their dual powertrain.
- Battery Replacement Costs: Over time, the battery may need replacement, which can be costly.
- Moderate Fuel Savings: Although more efficient than gas cars, HEVs save less fuel than fully electric vehicles (BEVs).
- Complex Maintenance: Dual power systems can make repairs more technical and sometimes more expensive.
Despite these challenges, HEVs remain a practical choice for drivers seeking reduced emissions and better fuel efficiency.
HEVs vs Traditional Vehicles
| Feature | HEV | Gasoline Car |
| Fuel | Gasoline + Electric | Gasoline |
| Emissions | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Moderate |
| Fuel Efficiency | High | Lower |
| Driving | Smooth, quiet | Standard engine noise |
This comparison highlights how HEVs offer a bridge solution between traditional cars and fully electric vehicles.
Future of Hybrid Electric Vehicles

The future of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) is promising as technology continues to advance. Improvements in battery efficiency, regenerative braking, and power management systems are making HEVs more fuel-efficient and affordable.
HEVs will continue to serve as a transition technology between traditional gasoline cars and fully electric vehicles, especially in regions where charging infrastructure is still developing. With smart features, eco-friendly designs, and lower emissions, HEVs are expected to remain an important part of the sustainable transportation revolution.
Conclusion
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) offer an effective balance between fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and convenience. By combining a gasoline engine with an electric motor, HEVs provide smoother driving, reduced fuel costs, and environmentally friendly transportation without the need for external charging.
While they face challenges like higher upfront costs and battery maintenance, continuous technological advancements make HEVs a reliable and practical option for eco-conscious drivers. For those who want to reduce their carbon footprint without fully switching to electric cars, HEVs are an ideal choice.
As the automotive industry moves toward sustainable mobility, HEVs will remain a key solution, bridging the gap between traditional vehicles and fully electric cars while promoting a greener and cleaner future.

